Digital asset security refers to the measures and practices used to safeguard digital assets such as cryptocurrencies, digital documents, and multimedia from unauthorized access, theft, or loss. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ether, and Bitcoin.com’s VERSE are ‘peer-to-peer.‘ This means you can send them anywhere in the world without asking for permission. It also means you – and you alone – are responsible for protecting your assets.
Like a vault protects physical assets, certain crypto wallets, such as the Bitcoin.com Wallet app, protect crypto assets – and in both cases, you need the right access key. However, since the Bitcoin.com Wallet app is self-custodial, no third party (neither Bitcoin.com, nor anyone else) holds the key. It’s just you. This means you have to be very careful about how you store your key. If you lose your key, you lose access to your crypto assets.
Below are some components and practices of good digital asset security.
What is Digital asset?
A digital asset is generally anything created and stored digitally, is identifiable and discoverable, and has or provides value. Digital assets have become more popular and valuable as technological advances integrate into our personal and professional lives. Data, images, video, written content, and more have long been considered digital assets with ownership rights.
Most digital items, like a company’s brand, can be assigned a value—monetary or intangible. Some digital items might only be valuable to the creator or one person, such as a family picture on your phone taken at a gathering. Others could be valuable to a much wider audience.
In the past, digital assets such as data or scanned documents were owned and used by organizations to realize value. However, digital assets were again redefined when blockchain and cryptocurrency were introduced in 2009. Anything in digital form became something that could be used to create value via tokenization on a blockchain.
Learn more about digital assets and how they are changing the way we view ownership, value, and our interactions.
How Does Digital asset security Work?
Digital asset security encompasses a variety of methods and technologies to protect cryptocurrencies and other digital assets from theft, unauthorized access, and other threats. Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
Security Measures:
- Cryptography: Cryptography plays a central role. Digital assets are secured using strong encryption algorithms that scramble data, making it unreadable to anyone without the decryption key (private key in the case of cryptocurrency).
- Secure Storage: Reputable custodians and wallets employ secure storage solutions for private keys and other sensitive data. This may involve hardware security modules (HSMs) or secure enclaves within computer systems.
- Access Controls: Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and strong password policies are implemented to restrict unauthorized access to digital assets. Some platforms may also use biometrics like fingerprint scanning for added security.
- Transaction Monitoring: Suspicious activity detection and transaction monitoring systems are used to identify and prevent potential fraud or hacking attempts.
Additional Security Practices:
- Regular Backups: Regular backups of data and private keys are crucial in case of system failures or security incidents. Backups should be stored securely, ideally offline.
- Software Updates: Keeping security software and wallet applications updated with the latest patches is essential to address any discovered vulnerabilities.
- Phishing Awareness: Educating users about phishing scams and best practices for protecting their login credentials is a vital security measure.
Roles and Responsibilities:
- Individuals: Cryptocurrency holders have a responsibility to choose reputable wallets, use strong passwords and MFA, and avoid clicking on suspicious links or downloading untrusted software.
- Custodians and Exchanges: Platforms that hold user’s digital assets have a significant responsibility to implement robust security measures, conduct regular security audits, and maintain adequate insurance coverage.
- Regulatory Bodies: Governments and regulatory bodies are increasingly developing frameworks to oversee digital asset security and address emerging threats in the industry.
Importance of Digital Asset Security:
- Financial Loss: Theft of digital assets can result in significant financial losses for individuals and businesses.
- Reputational Damage: Security breaches on cryptocurrency exchanges or custodial platforms can damage their reputation and erode user trust.
- Market Instability: Large-scale security incidents can lead to market instability and a loss of confidence in digital assets.
Continuous Improvement:
Digital asset security is an ongoing process as new threats emerge. Security professionals and developers are constantly working to improve security protocols, identify vulnerabilities, and implement new preventative measures.
By employing a layered approach that combines technological solutions, user awareness, and best practices, we can create a more secure environment for digital assets.
Features and Benefits of Digital Asset Security
Digital asset security goes beyond just protecting cryptocurrencies. It’s a comprehensive strategy encompassing various features and benefits to safeguard a wide range of digital assets from unauthorized access, theft, and other threats. Here’s a breakdown of some key aspects:
Features:
- Cryptography: The foundation of digital asset security. Strong encryption algorithms scramble data, rendering it unreadable without a decryption key. This safeguards sensitive information like private keys in cryptocurrency wallets.
- Secure Storage: Reputable custodians and storage providers employ secure methods for keeping private keys and other critical data. This may involve Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) that isolate encryption keys within tamper-proof hardware or secure enclaves within computer systems.
- Access Controls: Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring multiple verification steps (e.g., password, fingerprint scan) to access digital assets. Strong password policies and access control lists (ACLs) further restrict unauthorized access.
- Transaction Monitoring: Advanced systems continuously monitor transactions for suspicious activity. This helps identify and prevent potential fraud or hacking attempts in real-time.
- Data Backups: Regular backups of data and private keys are essential for disaster recovery. Backups should be stored securely, ideally offline and geographically separate from primary storage to minimize risk from single points of failure.
- Security Patch Management: Keeping security software and applications updated with the latest patches is crucial to address newly discovered vulnerabilities that hackers might try to exploit.
Benefits:
- Financial Protection: Robust digital asset security safeguards your cryptocurrencies and other valuable digital assets from theft or unauthorized use, preventing significant financial losses.
- Enhanced Trust: Strong security measures build trust with users and customers. This is especially important for cryptocurrency exchanges, custodians, and other platforms that hold user’s digital assets.
- Market Stability: When digital asset security is prioritized across the industry, it fosters a more stable and trustworthy environment for everyone involved. This can lead to increased adoption and growth of the digital asset ecosystem.
- Reduced Risk: A comprehensive security strategy minimizes the risk of data breaches, reputational damage, and legal ramifications associated with security incidents.
- Compliance: As regulations evolve around digital assets, robust security measures help organizations comply with industry standards and best practices.
Additional Considerations:
- User Education: Educating users about best practices like strong password hygiene, phishing awareness, and avoiding suspicious links is vital for comprehensive security.
- Regular Security Audits: Regular security audits conducted by independent firms can identify potential weaknesses in security protocols and suggest improvements.
- Insurance Coverage: Having adequate insurance coverage for digital assets can provide some financial protection in case of a security breach.
Overall:
Digital asset security is a multi-layered approach that requires ongoing vigilance and adaptation. By implementing a combination of these features and fostering a security-conscious culture, individuals and organizations can safeguard their digital assets and contribute to a more secure digital asset ecosystem.
Understanding Digital Assets
Digital assets have morphed into more than the words, pictures, videos, audio, and documents we associate with the term. When Bitcoin was introduced in 2009, it brought with it the blockchain—a distributed public ledger secured by a consensus mechanism. The concept was not new because data itself had become a valuable digital asset that required security measures, management, and storage. Distributed ledgers and the information contained in them had been around for some time.
However, it was new to most people who lived and worked outside of data science, data management, data analysis, or any other field requiring large distributed data networks. For a digital asset to be considered an asset, it must first have the potential to create value in that it can be used in a manner that generates value for the owner. The digital asset should then be able to transfer ownership through purchase, gifting, or other means of giving the rights to someone else, along with the value the item can bring. It must also be discoverable or stored somewhere that it can be found.
Types of Digital Assets
There are many different types of digital assets. Here is a list of many of the familiar ones:
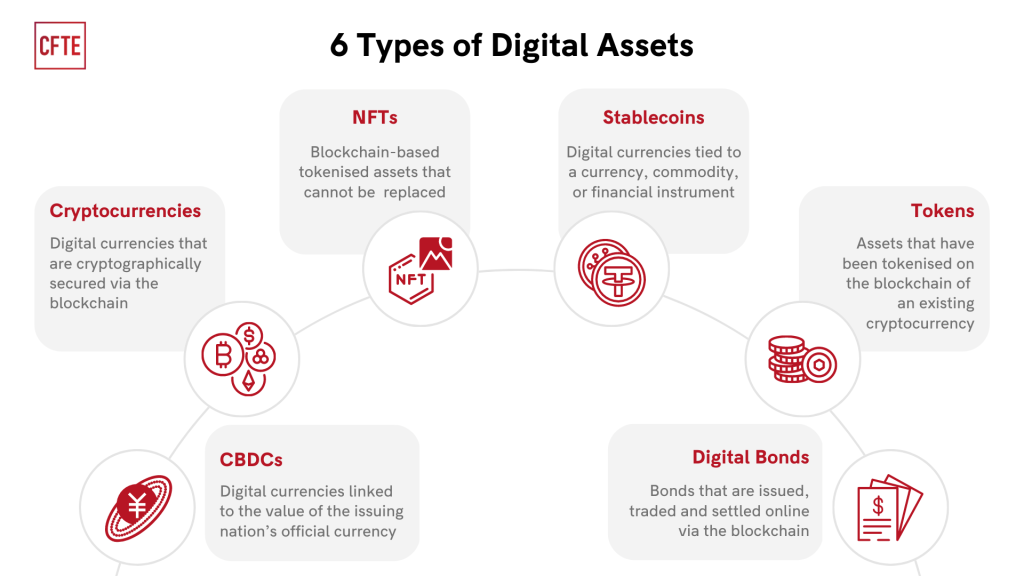
- Photos
- Documents
- Videos
- Books
- Audio/Music
- Animations
- Illustrations
- Manuscripts
- Emails and email accounts
- Logos
- Metadata
- Content
- Social media accounts
- Gaming accounts
Newer digital assets are based on blockchain or similar technologies:
- Nonfungible tokens
- Cryptocurrency
- Tokens
- Crypto Assets
- Tokenized Assets
- Security Tokens
- Central Bank Digital Currencies
Importance of Digital Assets
When you look at a list of the digital items that can be considered assets, it becomes clear that our lives are more digitally based than ever. For example, when we want to learn about something, we turn to digitally hosted information because it is quicker and easier than driving to a library, hoping they have the resources you need.
Our photos, entertainment, and important documents are mostly in digital form. Businesses and governments keep and store data and information, all of which have different values depending on how they can be used.
When investors, governments, and the general public became aware of blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies in the 2010s, digital assets took on an entirely new meaning. Cryptocurrencies joined the list of digital assets because people placed a value on them, whether they were intended to be used as assets or not.
Example of Digital Asset’s Impact
No matter what you do, your life is filled with digital assets. Here is an example of a digital asset enhanced day:
You wake up one morning and see that your favorite runningback has posted a sports video token of his winning touchdown in last year’s season, so you purchase it like a trading card from the past. You now own part of that moment.
At work, you used a cryptocurrency to buy sales data to analyze a specific market and sent a digital presentation of your findings to your boss, who forwarded it to management. It allowed them to make critical decisions and was filed away in the company’s digital storage vault.
On your way home, you were caught in a traffic jam and managed to take a once-in-a-lifetime video on your phone of the eagle that flew in your car window and sat down in your passenger seat. When you get home, you upload the video on an NFT marketplace and sell a few hundred NFTs for $1 a piece.
You then relax before bed by drawing on your graphics tablet. You draw the best stick figure sword fight you’ve ever seen and upload it to the same NFT marketplace, thinking it will have value someday to someone. Meanwhile, unbeknownst to you, your digital report was leaked to a competing firm, which is planning to use it to develop a competitive advantage over your company.
What Is an Example of a Digital Asset?
A digital asset is anything in digital form that can create value. You can still create something digitally, but it is not a digital asset if it has no value.
How Do Digital Assets Make Money?
Digital assets can make money if there is a demand for what they represent or what they are. You can sell them on an NFT marketplace, trade them on an exchange, or hold them and hope for a market price increase.
What Does the IRS Consider a Digital Asset?
The Internal Revenue Service considers any digital representation of value recorded on a blockchain a digital asset. This includes cryptocurrency, stablecoins, non-fungible tokens, and convertible virtual currencies.
Back up your wallet
Regularly back up your wallet data and store these backups in multiple secure locations. For hardware wallets, make sure to securely store the recovery seed phrase, which can be used to recover your assets if the wallet your device is on is lost or damaged.
The self-custody Bitcoin.com Wallet app makes it easy to back up your wallet. When you first install the Bitcoin.com Wallet app on your phone, you have the option of setting up biometrics or a PIN. This acts as the key to your wallet, but what happens if you lose or break your phone?
That’s why it’s important to “back up” your Wallet. Backing up your Wallet effectively means you’re creating an additional key and storing it separately from your phone. You can use that key to gain access to your Wallet from any device.
There are a few ways to back up your Wallet, but the easiest is surely the automated Cloud Backup Service. Here, you create a single custom password that decrypts a file stored in your Google Drive or Apple iCloud account. If you lose access to your device, you can reinstall the Wallet app on a new device, enter your password, and you’ll again have access to all your crypto assets. Here’s a video demonstrating how to set up the automated Cloud Backup:
Note: To use the automated Cloud Backup service, you’ll first need to login to either Google or Apple through the Wallet app.
Another way to back up your wallet is to create keys manually. With this method, you’ll be assigned a random set of 12 words (a “passphrase”). Then, when you reinstall the app on a new device, you’ll need to enter the 12-word passphrase to gain access to that wallet. Here’s a video demonstrating how to manually back up your wallets in the Bitcoin.com Wallet app:
Your Bitcoin.com Wallet app actually consists of multiple wallets, one for each of the blockchain networks we support. This means that at as minimum you have a BTC wallet, a BCH wallet, and an ETH wallet (at the time of writing). You can also create as many additional wallets as you want for those networks, as well as for the other networks we support (at the time of writing, those are Polygon and BNB Smart Chain). Critically, each new wallet you create will have its own backup key. For this reason, it can be extremely difficult to manage all your passphrases – and that’s exactly why we created the automated Cloud Backup services: It’s one simple password for all your wallets!
Use strong password management
Whether you choose a single password that decrypts your entire Wallet or multiple auto-generated 12-word passphrases corresponding to each wallet in your Bitcoin.com Wallet app, it’s essential that you adhere to password management best practices.
Firstly, you should never store your passwords in digital form, as doing so opens you up to the possibility of having them stolen by hackers. This includes taking screenshots or digital photos of your handwritten passwords.
For most people, the best strategy is to physically write down the password/passphrases on a piece of paper and store that paper somewhere safe. If the crypto assets in your Wallet are worth a lot, you’ll want to (manually) make copies of the paper, and store those copies in separate locations (eg. one at your house, one at a family member’s house).
While all of this may sound a little complex, it’s important to remember why it is so important: when you use a self-custodial wallet, you – and you alone – are in control of your funds.
Note that for manual backups, anyone with the passphrase can gain access to your wallet (and steal the assets in it) while for the cloud backup service, you have an extra layer of protection because an attacker will need to first get into your Google or Apple account, then enter the additional master password you created. If you set up your Google or Apple account with 2-Factor Authentication, you’re making it very difficult for hackers.
Disclaimer ||
The Information provided on this website article does not constitute investment advice ,financial advice,trading advice,or any other sort of advice and you should not treat any of the website’s content as such.
Always do your own research! DYOR NFA
Coin Data Cap does not recommend that any cryptocurrency Stocks Bonds should be bought, sold or held by you, Do Conduct your own due diligence and consult your financial adviser before making any investment decisions!





Leave feedback about this