What Is File Transfer Protocol (FTP)?
The term “file transfer protocol (FTP)” refers to a process that involves the transfer of files between devices over a network. The process works when one party allows another to send or receive files over the internet.
Originally used as a way for users to communicate and exchange information between two physical devices, FTP is now commonly used to store files in the cloud, which is usually a secure location that is held and accessed remotely. It may be used by a business or individual to transfer files from one computer system to another or by websites to upload or download files from their servers.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- File transfer protocol (FTP) is a way to download, upload, and transfer files from one location to another on the internet and between computer systems.
- FTP enables the transfer of files back and forth between computers or through the cloud.
- Users require an internet connection in order to execute FTP transfers.
- FTP is an essential tool for those who build and maintain websites.
- Many FTP clients are free to download, although most websites already have the FTP built in.
Table of Contents
How File Transfer Protocol (FTP) Works
File transfer protocol allows individuals and businesses to share electronic files with others without having to be in the same space. This can be done using an FTP client or through the cloud. Regardless of the option, both parties require a working internet connection.1
Most web browsers come with FTP clients that enable users to transfer files from their computer to a server and vice versa. Some users may want to use a third-party FTP client because many of them offer extra features. Examples of FTP clients that are free to download include FileZilla Client, FTP Voyager, WinSCP, CoffeeCup Free FTP, and Core FTP.
Many people have used FTP before without even realizing it. If you have ever downloaded a file from a webpage, you’ve used FTP. The first step is to log in, which may occur automatically or by manually inputting a username and password. FTP will also require you to access an FTP server through a specific port number. Once you access the FTP server through your FTP client, you can now transfer files. Not all public FTP servers require you to sign in because some servers enable you to access them anonymously.1
As noted above, FTP was originally developed as a way to send and receive files between two physical computers. But with advances in technology, users can execute file transfers through the cloud. Using the cloud allows transfers to be done conveniently anywhere and anytime, and at relatively low cost.2
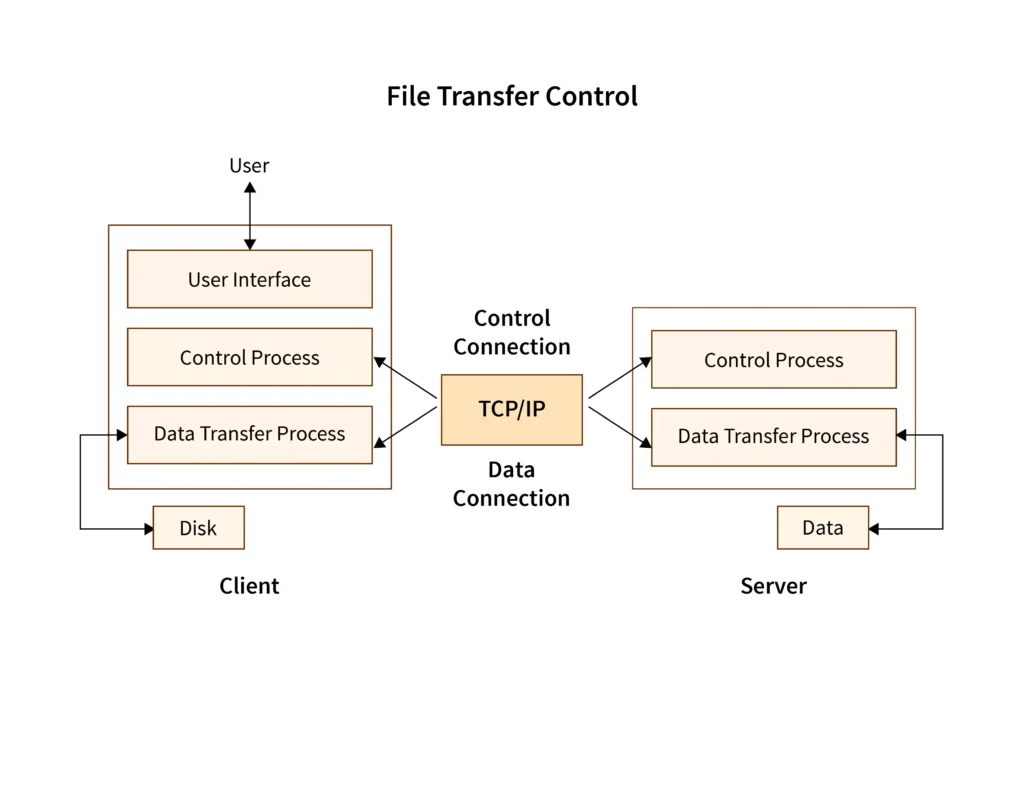
FTP Process
The FTP process can be broken down into just a few key steps.
- First, a user logs in to an FTP server (although a login might not be required).
- The FTP client interacts with the server upon a request, which is the second step.
- With FTP, a user can then upload, download, or move files on the server.
FAST FACT
The term “FTP client” refers to the software that allows you to transfer files to another party.
History of FTP
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) was first described in a white paper in 1971 by Abhay Bhushan, then a graduate student at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.3 The aim was to allow the transfer of data files over the ARPANET, the early precursor to the modern internet.
The original protocol has undergone several revisions and upgrades since the 1980s to improve its speed, fidelity, and security.
Types of FTP
There are various types of FTP, including anonymous and password-protected.
Anonymous file transfer protocol (FTP) allows the transfer of data without encryption or using a password. This is good for files that can be distributed without restrictions.
Meanwhile, password-protected FTP uses a username and password to access the files. FTP secure (FTPS) offers increased security when transferring, allowing for implicit transport layer security (TLS). FTP can also employ explicit TLS, which upgrades the connection to an encrypted connection for added security.
Other Protocols
File transfer protocol is one of many different protocols that dictate how computers and computing systems behave on the internet. Other such protocols include the following:
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP): Designed to transmit data across the web4
- Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP): Provides access to bulletin board or email messages from a shared service5
- Network Time Protocol (NTP): Synchronizes clock times on computers over a network6
File transfer protocol (FTP) enables computers on the internet to transfer files back and forth. As such, it is an essential tool for those building and maintaining websites today.
Benefits and Uses of FTP
FTP made handling data across the internet much easier and intuitive. Without File transfer protocol (FTP) and its later iterations, we would not be able to easily stream video content, make video calls, play online games, share files, or enjoy cloud storage.
Today, file transfer protocol (FTP) operates behind the scenes as a backbone for data transfer from servers around the world to millions of clients every second of every day.
Example of FTP Clients
File transfer protocol (FTP) software is relatively straightforward to set up. FileZilla is a free, downloadable FTP client. Other examples of FTP clients include Transmit, WinSCP, and WS_FTP.
You type in the address of the server you wish to access, the port, and the password for accessing the server. Once access has been granted, the user’s files on their local system will be visible, as will the accessed server.
The user can download files from the server to the local system, or upload files from the local system to the server. They can also make changes to files on the server, as long as they have the proper authorization to do so.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/filezilla-cb091304cca54cf0b494cfa02aba0e7d.jpg)
What to Look for in an FTP Client
Individual FTP clients provide different features that allow users to modify the way they upload and download files. For instance, if you use FileZilla, the program lets you set bandwidth limits for files. This enables you to control upload and download speeds, which can be helpful if you manage multiple file transfers at once.
Other features you may want to look for in an FTP client include public-key authentication, the ability to set file compression levels, or tools that enable you to search a server using file masks.
Does FTP Use TCP or UDP?
FTP uses transmission control protocol (TCP) for transport needs. It never uses user datagram protocol (UDP).
How Does FTP Work?
FTP allows for the transfer of files via the internet. FTP transfers require an internet connection. Downloading files means transferring a file from a server to a computer or device, while uploading is the opposite—transferring a file from a computer to a server.
What Is an Example of FTP?
Examples of FTP clients include CoffeeCup Free FTP, Core FTP, FileZilla Client, FTP Voyager, and WinSCP.
The Bottom Line
Now over 50 years old, file transfer protocol (FTP) is a critical piece of internet infrastructure that allows the quick and secure transfer of data online. Without FTP, we wouldn’t be able to enjoy many of today’s World Wide Web, from web-based online gaming to streaming to videoconferencing to the emerging metaverse.
Know more: https://gemini.google.com/app
Disclaimer ||
The Information provided on this website article does not constitute investment advice ,financial advice,trading advice,or any other sort of advice and you should not treat any of the website’s content as such.
Always do your own research! DYOR NFA
Coin Data Cap does not recommend that any cryptocurrency should be bought, sold or held by you, Do Conduct your own due diligence and consult your financial adviser before making any investment decisions!



