metaverse The early internet was almost entirely text based, with hyperlinks used to navigate between text pages. Over time it became more graphical until internet applications such as Gmail, Facebook, Instagram, etc, became the norm. All of this progress still has happened on screens (2-dimensional surfaces), but humans live in a 3-dimensional world.
The metaverse can be seen as the next stage in the evolution of the internet. The metaverse is the internet mediated by graphically rich 3D spaces with an increasing focus on virtual and augmented reality.
How Does metaverse Work ?
The metaverse is like a future version of the internet, but even more interactive. Imagine it as a collection of interconnected virtual worlds where people can exist as avatars and do all sorts of things. Here’s a breakdown of how it might work:
Building Blocks:
- VR and AR: Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are key technologies for the metaverse. VR headsets will immerse you completely in the virtual world, while AR overlays digital elements onto the real world. Think of VR like putting on a scuba mask for the internet, and AR like fancy sunglasses that show you extra information about the world around you.
- Networked Platforms: The metaverse won’t be a single world, but a network of interconnected ones. Each platform might have its own focus, like gaming, work, or social interaction. Imagine hopping between different islands in a massive online archipelago, each with its own unique features.
User Experience:
- Avatars: You’ll interact in the metaverse through an avatar, a digital representation of yourself. You can customize your avatar to look however you want, and it will be your way of navigating and interacting with the virtual world. Think of it like your online persona with a cool 3D body.
- Persistent and Real-time: The metaverse is envisioned as persistent, meaning it keeps running even when you log off. This allows for virtual worlds that evolve and change over time. It will also be real-time, so your actions and interactions will happen simultaneously for everyone involved. Imagine a virtual world that’s always bustling with activity, even when you take a break.
The Future is Open Ended:
- Decentralization vs. Centralization: There’s debate on how the metaverse will be structured. Some envision a decentralized metaverse where many companies contribute and users have more control over their data. Think of it like a giant community garden, where everyone contributes and shares. Others imagine a more centralized model, run by a few large companies. This would be more like a traditional theme park, with set rules and experiences.
The metaverse is still in development, and the specifics of how it will work are still being figured out. But the core idea is a persistent, interconnected virtual space where people can work, play, and socialize in new and exciting ways.
Metaverse Origins
The term metaverse was created by Neal Stephenson in his 1992 novel Snow Crash. In the novel, the metaverse is a virtual reality world, that according to Wikipedia, “appears to its users as an urban environment, developed along a single hundred-meter-wide road, the Street, that runs around the entire 65,536 km circumference of a featureless, black, perfectly spherical planet.” The metaverse is experienced from a first-person perspective via virtual reality goggles.
Pieces of the metaverse have existed up to this point. Below we go over a couple of these proto-metaverses.
Immersive games like Second Life, World of Warcraft, and Eve Online are what many conjure when they think try to imagine what the metaverse will be — and for good reason. All of these games have rich 3D worlds where your avatar can interact with others, but each has different focuses. Second Life focuses on social. World of Warcraft focuses on fun — it is first and foremost a game. Eve Online focuses on economy.
Social network platforms like Facebook, YouTube, and TikTok are not often thought of as proto-metaverses, but they are. Facebook is basically a mini-internet onto itself. While it is not graphically immersive, Facebook content has become increasingly image based. Facebook is in the process of becoming graphically immersive by pivoting hard into the metaverse, even going as far as rebranding as Meta. YouTube and TikTok are both social networks with a main emphasis on video, which is way more immersive than text.
Defining the Metaverse
The metaverse needs three equally important components: immersive graphical interfaces, interconnected networks, and cryptoassets. Where two circles overlap, you get an incomplete metaverse. Only when all three overlap in the center do you get a fully formed metaverse. Let’s look at all of the different categories and overlaps.
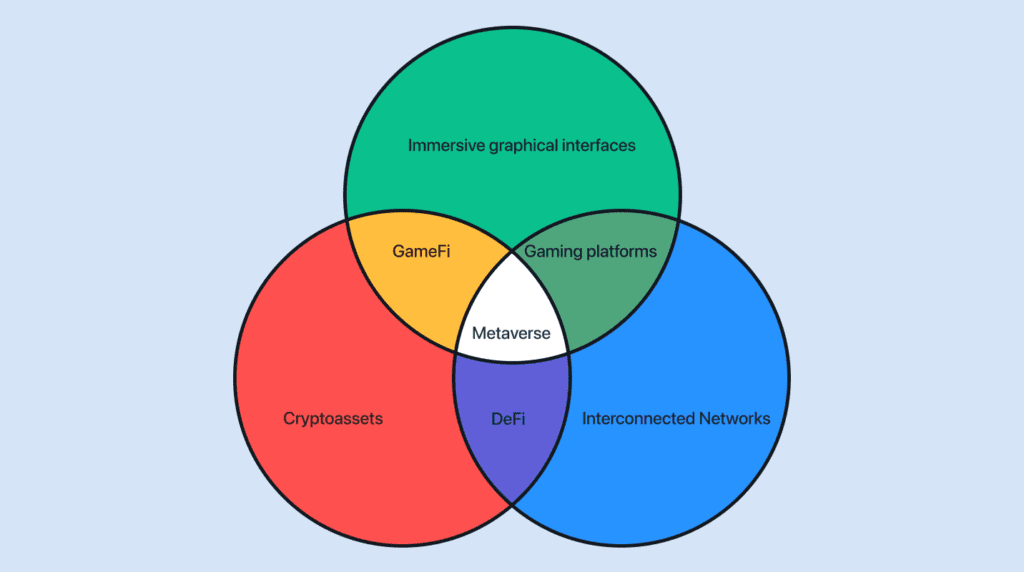
Immersive graphical interfaces
Many articles explaining the metaverse claim that virtual or augmented reality are necessary for a metaverse. This is simply not true. If that technology matures enough to be as integral to life as a smartphone, virtual or augmented reality might become the accepted way to interact in the metaverse, but it doesn’t have to be. Plenty of 3D games provide an immersive gaming experience.
Interconnected networks
this is another way to say, “the internet,” which is a globe-spanning hodgepodge of networks glued together. Some parts of the internet are more controlled than others, like those in authoritarian countries. Large parts of the internet are walled off, like the data in Facebook. The metaverse will be just as diverse as the internet today. Some parts will be wild and unfettered. Others will be manicured and highly controlled.
Cryptoassets
Cryptocurrencies and other digital assets provide a money layer as well as a way to create digital scarcity. Digital scarcity suddenly makes it possible to have online digital ownership, a crucial component of a persistent world online. Digital ownership allows people to traverse the disparate networks that make up the current internet while maintaining a cohesive self-custodied personality.
GameFi
A cross between immersive graphical interfaces and crypto assets, GameFi are games that integrate crypto assets into the game mechanic loop. The first breakout category of games from this mix are Play-to-earn (P2E) games, such as Axi Infinity.
GameFi is still very young, and most of the games seem less about having fun, and more about making money. Expect this to change over time as more traditional game companies get involved. Games have become more and more a social experience, and one that has over time pushed more and more into the physical world. Practically every game made these days has a multiplayer component, or it fails outright. Games like Pokemon Go! require traversing the physical world in order to play. Expect this trend to accelerate in the metaverse.
Gaming platforms
A mix of immersive graphical interfaces and interconnected networks yields things like gaming platforms and MMORPGs. Platforms like Steam and Epic Game Store are less graphically immersive, but very interconnected. This is changing with things like Steam’s VR interface. They include PC, MAC, and mobile networks, featuring thousands of games, a social network, review sites, and individual stores. MMORPGs are very immersive graphical interfaces to fantastical worlds. Games such as World of Warcraft and EVE Online are feature rich worlds. EVE Online especially could count as a gaming platform as it features a complex economy.
DeFi
Cryptoassets spread across interconnected networks, or blockchains, makes up DeFi. DeFi is building an alternative financial system parallel to the legacy financial system. DeFi replicates much of the financial tools and services the legacy financial system gives people access to, but the legacy financial system predominantly gives access to people in developed countries.
Metaverse: Combine immersive graphical interfaces, interconnected networks, and cryptoassets, you get the future of the internet. An internet much like the one we have now, but with more personal power, naturally intuitive interfaces (for humans), and the place that more and more will intrude on the physical world.
How Crypto Fits into the Metaverse
Crypto was the last missing component of the metaverse. Crypto introduced the idea of digital scarcity, which enables digital ownership. Many components of crypto will play pivotal parts in the metaverse.
Asset management
Using crypto wallet software, you can self-custody your online data and digital assets. As of right now, each internet-based company owns your data. This includes text and photos, but also things like your social graph — the unique mesh of connections and reputation you’ve built up on that service. You might be able to download your text and data, but the social graph is non-transferable. These internet companies do not interoperate, so your online presence is fragmented and uneven across all of the various internet platforms. Crypto asset management allows you to control your data and use it across any service that supports it.
Controlling your data is very important when that data takes the form of cryptoassets, which can be worth tens, or hundreds, or millions of dollars!
Cryptocurrencies
Crypto assets that are money-like, for example Bitcoin and stablecoins, will be an important part of an online-first economy. Games like Eve Online or services like Steam have money-like digital assets, but the “money” is controlled one hundred percent by the company. The company can create, destroy, or revoke that money whenever they want. On top of that, the company can go bankrupt, or decide to deprecate the game in favor of a sequel. Cryptocurrencies are widely accepted outside of one companies’ ecosystem. They are also cross-border.
NFTs
NFTs allow you to self-custody your digital assets — from clothes and weapons for your avatar, to pieces of real estate in virtual worlds. They can represent digital art such as photos, music, and videos. They can even act as tickets to special invite-only virtual worlds, games, guilds, and communities. People are only just beginning to explore how to use NFTs. Just like with the internet in the 90s, it’s difficult to imagine how it will be used ten years in the future.
Features and Benefits of Metaverse
The metaverse is still under development, but it has the potential to revolutionize the way we live, work, and play. Here are some of its key features and benefits:
Features
- Immersive experiences: The metaverse will allow us to experience things in a way that is not possible in the real world. For example, we could visit a museum in Paris or climb Mount Everest, all from the comfort of our own homes.

- Customization Users will be able to create and customize their avatars, which will be their digital representations in the metaverse. Avatars can look however the user wants them to look, and they can be used to express oneself in new ways.
- Social interactions: The metaverse will allow us to connect and socialize with other people from all over the world in real-time. We can meet up with friends and family, attend virtual events, or even start new relationships.
Benefits
- Enhanced communication and collaboration: The metaverse can help us to communicate and collaborate with others in more effective ways. For example, businesses can use the metaverse to hold virtual meetings, train employees, or develop new products.
- New educational and training opportunities: The metaverse can be used to create new educational and training opportunities. For example, students can take virtual field trips to historical landmarks or attend classes in a simulated environment.
- Economic opportunities: The metaverse will create new economic opportunities. For example, businesses can sell virtual goods and services, and users can create and sell their own digital assets.
metaverse
The metaverse is still in its early stages of development, but it has the potential to change the way we live, work, and play. It is important to note that there are also potential risks associated with the metaverse, such as addiction and privacy concerns. However, if we develop the metaverse in a responsible way, it has the potential to be a force for good in the world.
metaverse User Experience?
Metaverse user experience (UX) is all about crafting a seamless and immersive experience for users in this virtual world. Here are some key aspects to consider:
Immersion:
- Visually Stunning Environments: Imagine high-fidelity graphics, realistic lighting, and spatial sound that transports you to another world.
- Natural Movement and Interaction: Intuitive controls that mimic real-world movements for a fluid experience. This could involve using VR controllers or even advanced wearables that track your body language.
Customization and Identity:
- Personalized Avatars: The ability to create detailed avatars that reflect your personality or even go beyond physical limitations. Want to be a blue-skinned alien with wings? The metaverse offers that freedom.
- Digital Ownership: Potentially owning virtual clothes, accessories, or even real estate within the metaverse. This can add a layer of personalization and investment to your experience.
Social Interaction and Connection:
- Real-time Communication: Imagine high-quality voice chat and expressive avatars that convey emotions, creating a more natural feeling of social interaction.
- Shared Experiences: The ability to attend virtual events, play games together, or simply hang out with friends in immersive settings. Imagine attending a concert in Paris or exploring a virtual museum with colleagues, all from the comfort of your home.
Usability and Accessibility:
- Intuitive Interface: User interfaces that are easy to learn and navigate, even for those not familiar with VR or AR technology.
- Multilingual Support: Catering to a global audience by offering interfaces and experiences in various languages.
- Accessibility Features: Ensuring the metaverse is accessible to users with disabilities, so everyone can participate.
Safety and Security:
- Privacy Protections: Safeguarding user data and ensuring control over how your avatar and information are used within the metaverse.
- Anti-Harassment Measures: Creating a safe and inclusive environment with measures to prevent harassment and abuse.
Metaverse UX is a complex but exciting field that will continue to evolve as technology advances. By focusing on these aspects, designers can create a truly engaging and enjoyable experience for everyone in this virtual world.
Is Metaverse Safe?
The metaverse is a developing concept, and safety is a major concern. Here’s a breakdown of the potential risks and what’s being done to address them:
Safety Concerns:
- Privacy: There are worries about user data collection and how it might be used within the metaverse. Avatars could collect a lot of information about our movements and preferences, raising privacy concerns.
- Security: The metaverse could be vulnerable to hacking and cyberattacks, potentially leading to financial losses or theft of virtual assets.
- Addiction: The immersive nature of the metaverse could lead to addiction, with users spending excessive time neglecting real-world responsibilities.
- Harassment and Abuse: The anonymity of virtual spaces can embolden some to harass or bully others. New forms of online abuse could emerge in the metaverse.
- Physical Health: Excessive use of VR headsets could lead to eye strain, dizziness, and even social isolation if neglecting physical activity.
Safety Efforts:
- Regulation: Governments and organizations are starting to discuss regulations for the metaverse to protect user privacy and safety.
- Platform Security: Metaverse platforms are working on security measures to prevent hacking and fraud.
- User Education: Educating users about online safety practices and responsible metaverse use is crucial.
- Community Guidelines: Developing clear community guidelines and reporting mechanisms to address harassment and abuse.
- Balance and Breaks: Encouraging users to take breaks and maintain a healthy balance between virtual and real-world activities.
Who’s Responsible?
- Tech Companies: Metaverse platform developers have a responsibility to build in security features and user protections.
- Governments: Regulation is needed to ensure fair practices and prevent misuse of user data.
- Users: We all have a role to play in practicing responsible behavior and being aware of potential risks.
The Future of Metaverse Safety
The has the potential to be a fantastic tool for connection and creativity, but safety needs to be a top priority. By working together, tech companies, governments, and users can create a safe and enjoyable experience for everyone.



